Manual for the protection against fire of load bearing structures (part 1)
Today we will offer a quick answer on how to fireproof the principal types of load bearing structures when they are not equipped against fire, to keep them from collapsing, at least for the time necessary to their evacuation.
But first, let us define the four principal types of load bearing structures that we can find in new constructions and renovations:
- Reinforced concrete structure.
- Steel structure.
- Wooden structure.
- Concrete or wooden structure with metallic reinforcement.
REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURE:
It is the most common load bearing structure. Generally, this structure is conceived in a way that is aligned with the applicable standards of resistance to fire, but in certain cases as renovations or changes of building use, the structure might not meet the requirements. The main requirements are usually about two things:
- The distance between the side exposed to the fire and the steel frames.
- The minimal thickness of the structural element.
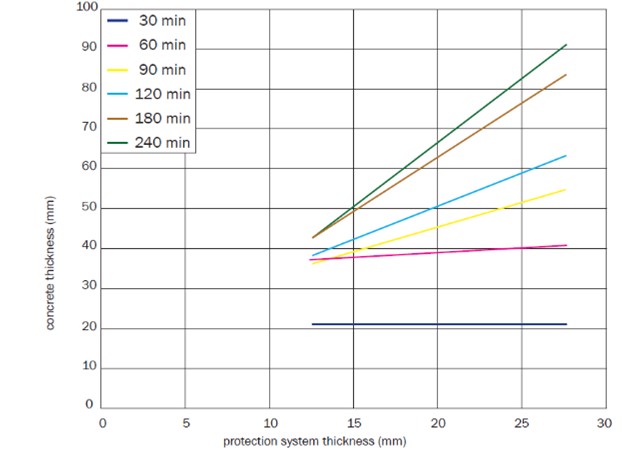
Once we know the required time of fire resistance, we can determine whether the concrete thickness is adequate or if it is necessary to reinforce the structure, in order to be in line with the present regulations. If the structure is not in line with the regulations, it is possible to install protective layers that have been tested under the European Standard EN 13381-3: 2016 Methods to determine the contribution to fire resistance of structural elements. Part 3: Protection applied to concrete elements. Those tests will help us determine the equivalent thickness we will need to apply.
mercor tecresa® has tested 3 different products for said protection:
- Tecwool F® Mortar: It is a mortar made of mineral wool and cement. Its easy application and its low cost make it the most used solution. The next table shows the equivalent thickness according to the required time of fire resistance.
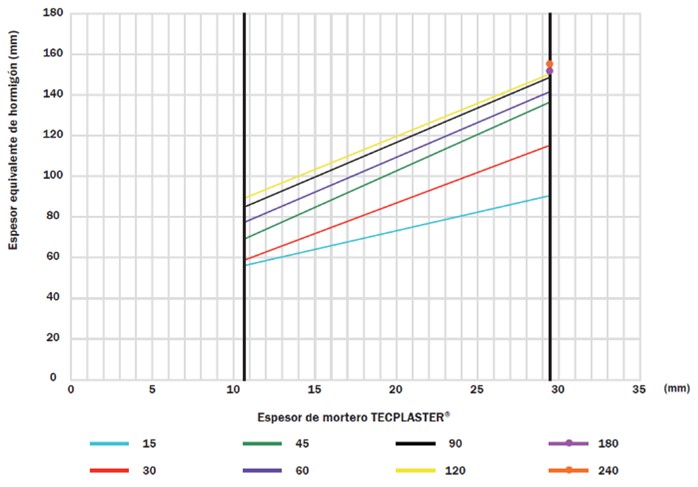
- Tecplaster® Mortar: It is a mortar prepared with a base of gypsum, perlite and vermiculite that provides a high protection against fire with a small thickness:
- Tecbor® Board: it is a rigid board made of magnesium oxide that can be fixed directly to the beam or the pillar to ensure that the structure counts with the required fire resistance. The installation work is more important, but the finish is better than the previous products.
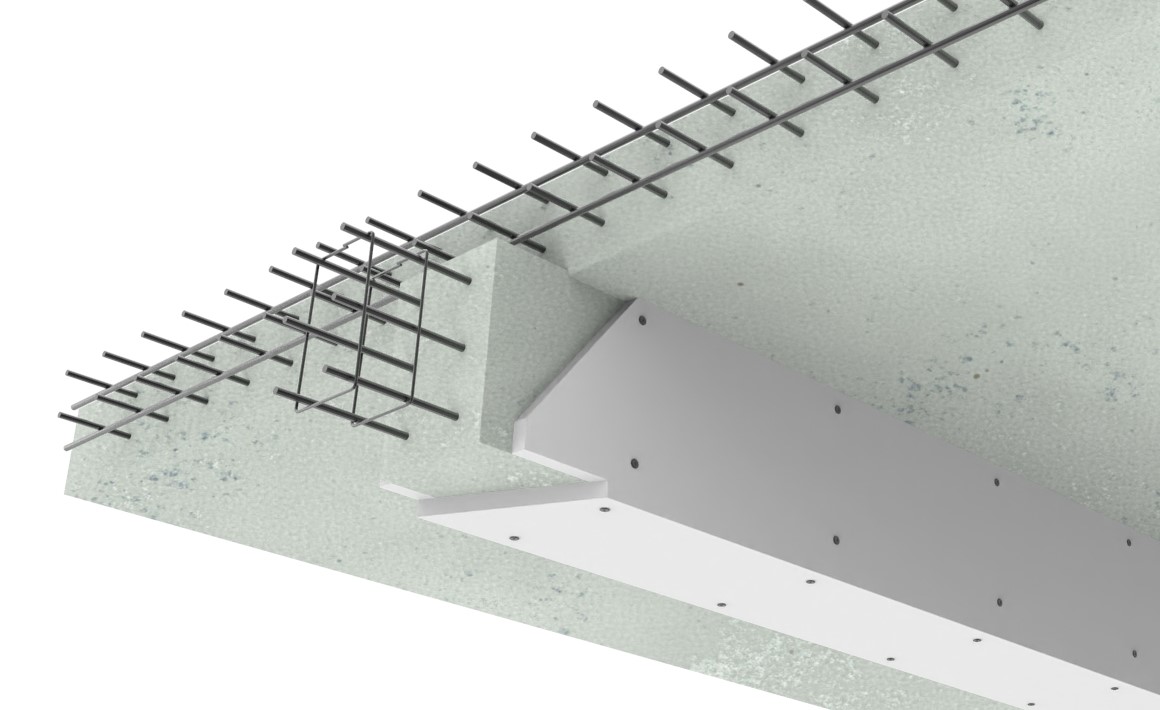
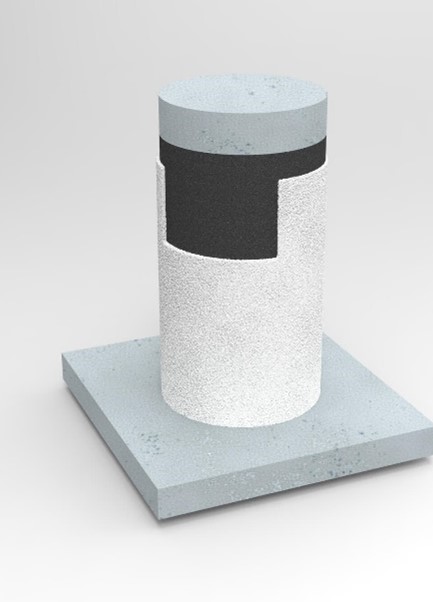
In certain cases, when the structure meets the fire resistance requirements but fails mechanically, the concrete is reinforced with Carbon fibre. The problem with this solution is that at 100ºC the resin that agglutinates the fibres becomes viscous and loses its reinforcement purpose, leading to the collapsing of the structure. To avoid this problem, Mercor Tecresa has designed a solution where a 50mm thick layer of Tecwool F® mortar is applied, so that the Carbon fibre does not reach its critical temperature of 81.4ºC, for at least 2 hours after the fire has started.