UNE 23585: Changes in the standard
Actualizado a fecha: 2 December, 2018
Modifications for the calculation and design methods for a smoke exhaust system
Last November, the UNE 23585 standard, in force since 2004, was modified with several corrections and updates. These are the most significant ones included in the new regulations already in effect:
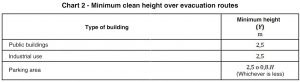
Minimum height on the evacuation route
On spaces open to the public, the minimum height now is set to 2.5m instead of 3m.
Rapid Response Sprinklers such as ESFR
They weren’t contemplated in the old standard and, for calculation purposes, they were considered like ceiling sprinklers and intermediate levels. The new standard specifies that they should be considered as ceiling sprinklers, regardless of whether they are quick response or not.
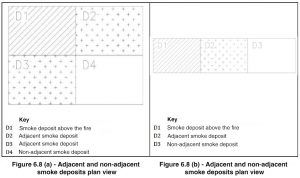
Replacement air
There is also a clarification regarding the replacement air when it comes from adjacent smoke deposits. Sometimes, to improve the calculation, all the smoke deposits that were located next to the studied one were considered, including the one that was joined with a single vertex. Now, specify more precisely which deposit can be counted when talking about the contribution of air in relation to the aerodynamic surface of smoke extraction AvCv.
Inclement weather
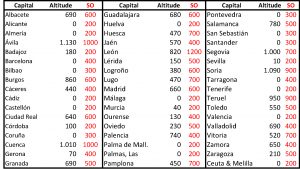
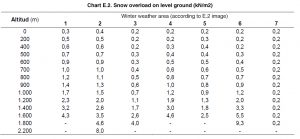
Finally, there is also an update on the regulations related to this matter as recalled in the CTE-DBSE, Building Standard. This affects, above all, the values of Snow Overload (SO) of the ventilators, with the below figures by provincial capitals:
Snow Overload by provincial capitals:
Snow overload by geographic area and altitude